Studies have found that extracellular matrix can control cell movement by regulating the sugar consumption of cells

Studies have found that extracellular matrix can control cell movement by regulating the sugar consumption of cells

Copyright © iCell Bioscience Inc, Shanghai 2018-2019
Researchers at UCLA have found that extracellular matrices can control the movement of cells in the body by regulating the sugar consumption of cells. The extracellular matrix is a dense network of proteins and carbohydrates around the cells. The study found that a sharp change in the single component of the extracellular matrix promotes rapid changes in cell metabolism and migration.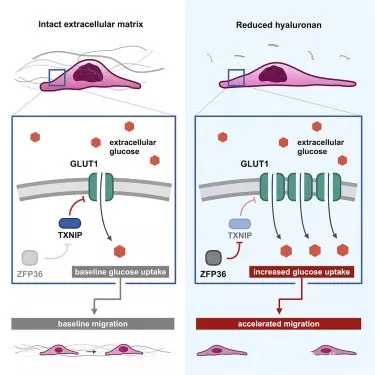
Considering the importance of glucose metabolism in the growth and migration of cancer cells, scientists have conducted in-depth research on how glucose metabolism is responsive to internal and external stimuli, but few studies have focused on metabolism and extracellular matrix. The relationship of compositional changes, while changes in extracellular matrix components occur during normal development and disease progression.
By analyzing patients' breast cancer tissues and genes affecting glucose metabolism in breast cancer cell lines, researchers have discovered that one of the genes closely related to the high-speed metabolism of glucose is a receptor for the transparent acid of the core component of the extracellular matrix. . Since this receptor associates cells with hyaluronic acid in the extracellular matrix, this study suggests that changes in the composition or structure of the extracellular matrix may affect metabolism. The researchers validated their conjecture by regulating the level of hyaluronic acid around the cells and measuring the subsequent glucose metabolism levels of the cells.
The study suggests that scientists may be able to create new ways to treat cancer by targeting cancer cells to sever the ability of cancer cells to metabolize sugar. In addition to therapies that directly target cancer cells, researchers can also alter tumor metabolism by targeting extracellular matrices.
This research will also broaden people's awareness of a range of diseases, especially to reveal how cancer cells spread. It suggests that the ability of cancer cells to consume different levels of nutrients in a single tumor tissue may be related to their ability to migrate. Cells with high rates of glucose metabolism may cause them to migrate to other parts of the body, that is, metastasis.
 Loading ....
Loading ....
