Neuronal Tracing Tools
Neuronal Tracing Tool Services
Various synapses connect neurons in the brain, resulting in the complex activities of the brain. To gain a deeper understanding of the function of the brain, it became necessary to develop the technology to dissect the brain circuits. Currently, conventional tracers and recombinant viral vectors are used to study brain circuits. Tracers such as CTB, HRP, PHA-L, BDAs, and so on, have some disadvantages, including the following:1) It is not possible to achieve cell specificity.
2) The efficiency of the system is not stable.
3) A circuit involving multiple steps of synaptic connections can not be realized.
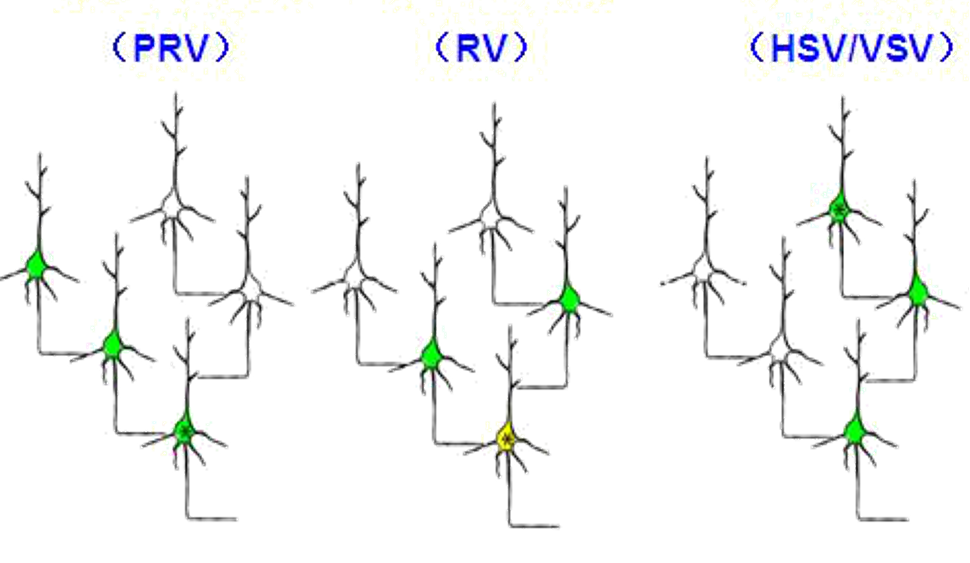
Genetically engineered recombinant viral vectors have, however, proven to be powerful tools for visualizing neural connectivity due to their ability to enter cells and deliver a variety of genes efficiently. The commonly used neurotropic virus, such as HSV ( Herpes simplex virus type 1), VSV (Vesicular stomatitis virus), PRV (pseudorabies virus), and RABV (rabies virus) can cross synapse from one cell to another if we provide the protein that used for replicate. Additionally, SFVs (which mark the fine morphology of in-situ neurons), as well as AAVs (used as helper viruses to express exogenous genes or as monosynaptic tracers), can also be used.

Advantage
- ● Fast and high efficiency
- ● Strong background in a neuronal tracing tool
- ● Hypotoxicity and strong signal
- ● The most competitive price
We offer AAV, VSV, PRV, and RABV, and HSV services to promote neuronal tracing studies.
Table 1 Recombinant viral vectors commonly used in neural circuit tracing
| Type | Virus name | Classification | Genomic type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non- transsynaptic | Adeno-associated virus, AAV | Parvoviridae | Single-stranded DNA | ||
| Canine adenovirus, CAV | Adenovirus | Double-stranded DNA | |||
| Semliki Forest virus, SFV | Togaviridae | + Single-stranded RNA | |||
| Rabies virus (Glycoprotein G-deleted), RV-∆G | Rhabdoviridae | -Single-stranded RNA | |||
| Herpes simplex virus amplicon, HSV amplicon | Herpesviridae | Double-stranded DNA | |||
| Trans-synaptic | Trans multisynaptic | Anterograde, multisynaptic | Herpes simplex virus, HSV H129 | Herpesviridae | Double-stranded DNA |
| Vesicular stomatitis virus, VSV | Rhabdoviridae | -Single-stranded RNA | |||
| Retrograde, multisynaptic | Pseudorabies virus, PRV | Herpesviridae | Double-stranded RNA | ||
| Rabies virus, RV WT | Rhabdoviridae | -Single-stranded RNA | |||
| Trans-monosynaptic | Anterograde, monosynaptic | Herpes simplex virus (TK-deleted), HSV-∆TK | Herpesviridae | Double-stranded DNA | |
| Adeno-associated virus, serotype 1, AAV1 | Parvoviridae | Single-stranded DNA | |||
| Retrograde, monosynaptic | Rabies virus, RV-∆G-EnvA | Rhabdoviridae | -Single-stranded RNA | ||
| Pseudorabies virus (TK-deleted), PRV-∆TK | Herpesviridae | Double-stranded RNA | |||
 Loading ....
Loading ....
