Efficient transduction of Retinal tissue with rAAVs vectors
Efficient transduction of Retinal tissue with rAAVs vectors
The eye is the most important organ of the human senses. Compared with other organs, the eye is small, relatively closed, and away from other tissues. Eye diseases are complex, and the rise of gene therapy offers hope for the treatment of inherited eye diseases (retinitis pigmentosa, Leber congenital amaurosis, etc.), even pathological eye diseases (retinopathy, etc.), and other eye diseases (optic nerve damage).Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is an ideal gene transfer vector tool in gene therapy of eye diseases due to its advantages such as good safety, wide host range, low immunogenicity. At present, there are at least 9 serotypes of AAV used for gene transfer in the eyes, and each serotype of AAV has different infection efficiency for different tissues and cells. To more efficiently and specifically infect the retina and retinal Mueller cells, the scientists developed retinal-specific serotype AAV-ANC80L65 and retinal Mueller cell-specific serotype AAV-SHH10 by analyzing capsid proteins of existing serotypes.
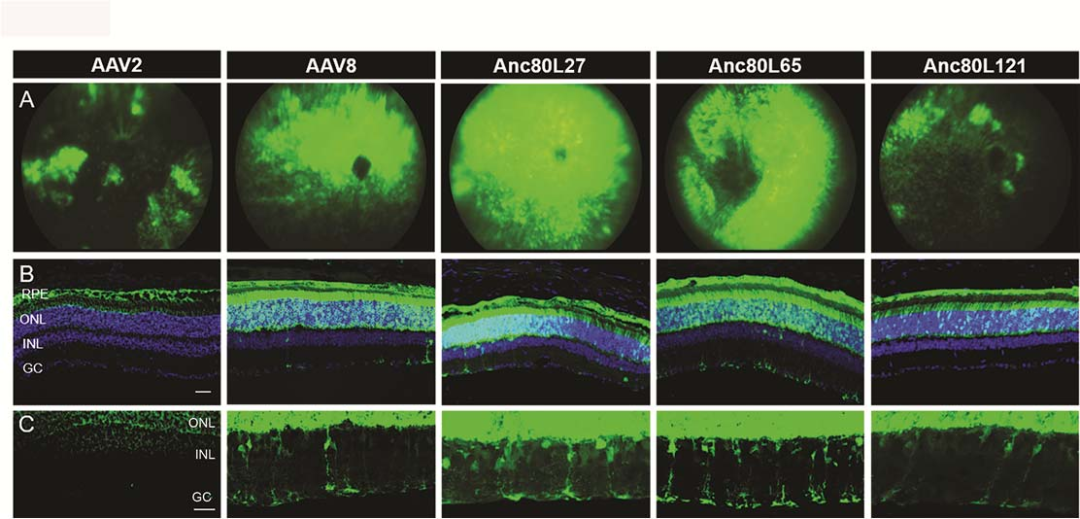
1:rAAVs serotype anc80L65 vectors highly infected with retina in vivo.
Reference:Synthetic adeno-associated viral vector efficiently targets mouse and non-human primate retina in vivo.AAV2, AAV8, Anc80L27, Anc80L65, and Anc80L121 were injected into male C57Bl/6 mice (6-8 weeks old) at equal doses. The expression of the EGFP fluorescent protein was monitored through fundus imaging of the retina after 4 weeks post-injection. Results show Muller glia transduction for all serotypes, except AAV2, and for Anc80 variants, a number of additional neuronal retinal cell types were clearly GFP positive.

Fig1.Comparison of transgene expression after subretinal delivery using Anc80 variants, AAV8 and AAV2. (A. Fundus imaging in eyes B. Confocal images of retinal cryosections for transduction comparison of RPE and photoreceptors cells. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; ONL, outer nuclear layer;INL, inner nuclear layer; GC, ganglion cells. C. Magnification of the INL area (in the middle panel of B) to
show transduction of inner nuclear neurons and glia.)
Since many applications of retinal gene therapy rely on effective transduction of cone photoreceptors, these specialized cells are responsible for high sensitivity and color vision, effective cone cell targeting is essential for retinal gene therapy. Therefore, the author also compared the transduction efficiency of Anc80 variant and other serotypes in cone cells and the expression time in vivo.
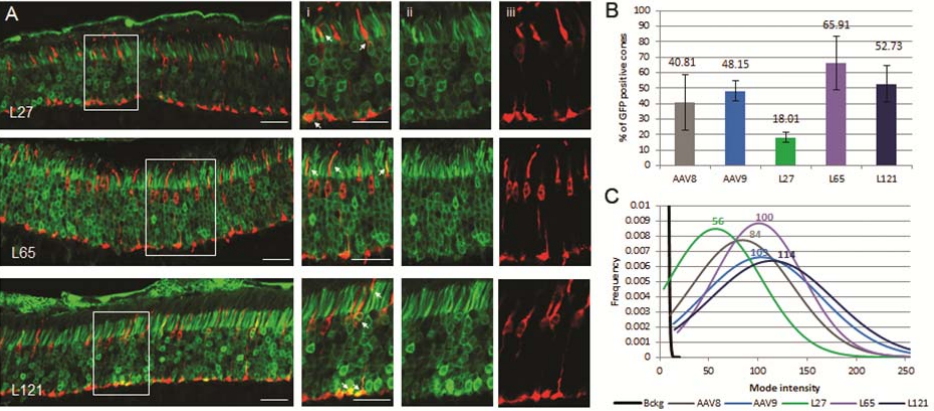
The results showed that in the mouse retina, Anc80L65 had higher cone-light receptor affinity than other AAVs. Finally, the Anc80L65 showed the same effect in rhesus monkeys. The results support the use of Anc80L65 for retinal gene delivery therapy.

The results showed that in the mouse retina, Anc80L65 had higher cone-light receptor affinity than other AAVs. Finally, the Anc80L65 showed the same effect in rhesus monkeys. The results support the use of Anc80L65 for retinal gene delivery therapy.
2: rAAVs serotype shH10 vectors highly infected with retinal muller cell in vivo
Dystrophin-Dp71 being a key membrane cytoskeletal protein, which is mainly localized in Muller cells and more specifically in their inner endfeet, around retinal vessels, closely related to the blood-retinal barrier (BRB). The author used AAV with serotype shH10 to restore Dp71 expression in Muller cells of the Dp71 deficient mouse. The result shows that strong and specific expression of exogenous Dp71 in Muller cells and restores all protein interactions to re-establish a proper functional BRB and retina homeostasis.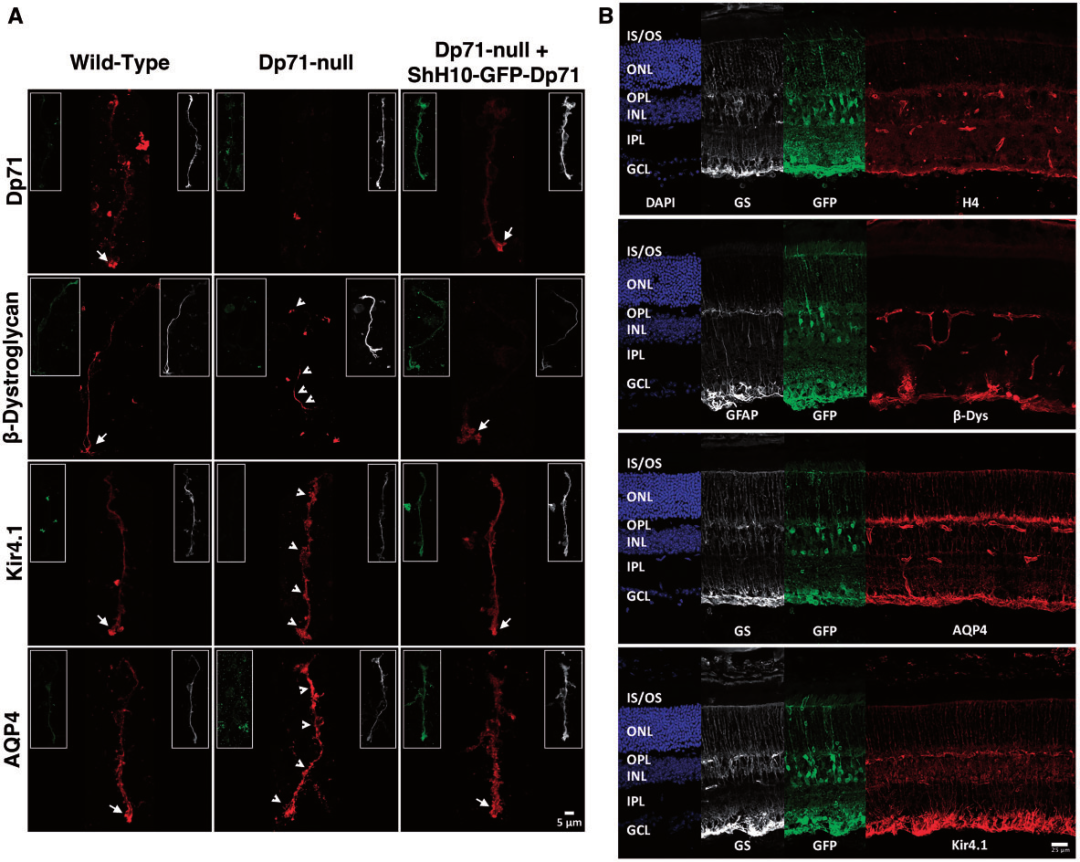
Fig3. A. Relocalization of Dp71 and Dp71 related proteins in the Muller glial cells.
B. Retinal cryosections of Dp71-null mice retinas after Dp71 restoration.
1. Synthetic adeno-associated viral vector efficiently targets mouse and non-human primate retina in vivo.Livia S Carvalho, Ru Xiao, Sarah Wassmer, Aliete Langsdorf, Eric Zinn,Simon Pacouret, Samiksha Shah,Jason I Comander, Leo Kim, Laurence . DOI: 10.1089/hum.2017.154
2. AAV-mediated gene therapy in Dystrophin-Dp71 deficient mouse leads to blood-retinal barrier restoration and oedema reabsorption. Ophelie Vacca1, Hugo Charles-Messance, Brahim El Mathari1,Abdoulaye Sene, Peggy Barbe, Ste´phane Fouquet, Jorge Aragon, Marie Darche,Audrey Giocanti-Aure´gan, Michel Paques,Jose´-Alain Sahel, Ramin Tadayoni, Cecilia Montanez, Deniz Dalkara and Alvaro Rendon. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw159.

Frequently Asked Questions: AAV Service
1. What is recombinant AAV (rAAV)?
2. What's the cloning capacity for rAAV?
3. Is recombinant AAV replication deficient?
4. Is AAV stable? What is the recommended storage temperature?
Request more info
Support
If you have any questions about plasmid vector construction services, just email us at [email protected] or call us at 866-986-9598.
 Loading ....
Loading ....
